The safety of our drinking water is often taken for granted, but recent research reveals a troubling reality: toxic chemicals are alarmingly prevalent in US water sources. From arsenic to PFAS, these contaminants pose serious health risks, yet many remain unaware of the dangers lurking in their taps. In this article, we delve into the specific toxic chemicals in US drinking water, from their sources, health impacts to practical solutions for relief and safeguarding our water supply.
Prevalence of Toxic chemicals in US Water
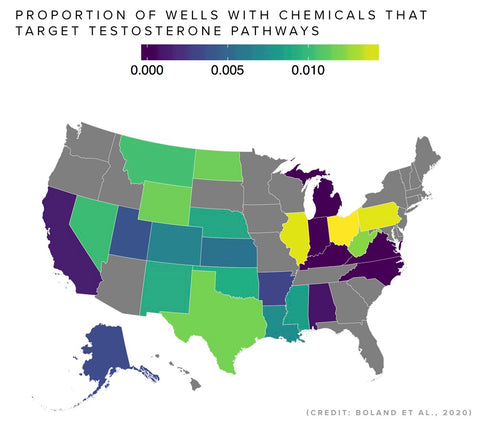
A study led by University of New Mexico researcher Johnnye Lewis reveals widespread presence of toxic contaminants in US drinking water, posing health risks, including cancer. Seven main contaminants were identified: arsenic, fracking fluids, lead, nitrates, chlorinated disinfection byproducts, PFAS, and uranium. Many of these are carcinogenic or linked to various health issues. Disproportionate impacts are observed on tribal lands and minority communities. Climate change exacerbates the challenge of finding clean water sources, especially in the western US, amplifying risks for underserved areas. Urgent action is urged to upgrade infrastructure, enhance water treatment, and strengthen safety standards.
4 Kinds of Common Contaminants in US Drinking Water
In the United States, several common contaminants frequently find their way into drinking water sources, posing serious health risks to consumers. Understanding these contaminants is crucial for ensuring the safety of our water supply. Below, we explore four prominent pollutants:
1. Arsenic
Arsenic is a naturally occurring element found in soil and rocks, often leaching into groundwater. Chronic exposure to arsenic in drinking water has been linked to various health issues, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and skin problems.
- Source
Natural Occurrence: Arsenic is naturally present in the earth's crust and can leach into groundwater from geological formations.
Industrial Activities: Certain industries, such as mining, smelting, and coal burning, can release arsenic into the environment, contaminating water sources.
Agricultural Practices: Pesticides and fertilizers containing arsenic compounds can contribute to contamination through runoff and leaching into water bodies.
- Potential Health Risks
Chronic exposure to arsenic in drinking water poses significant health risks, including an increased risk of cancer (such as skin, lung, bladder, and kidney cancer), cardiovascular disease, and skin lesions. Long-term ingestion of arsenic-contaminated water has also been linked to neurological issues, developmental delays in children, and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
2. Lead
Lead contamination often stems from aging infrastructure, such as old pipes and plumbing fixtures. Exposure to lead can cause developmental delays in children, as well as cardiovascular and neurological problems in adults.
- Source
Aging Infrastructure: Lead pipes, solder, and plumbing fixtures in older buildings can corrode over time, releasing lead particles into drinking water.
Industrial Processes: Lead contamination can result from industrial activities such as metal processing, battery manufacturing, and mining.
Lead-Based Paint: Lead-based paint used in older homes can deteriorate and contaminate soil and water sources, posing a risk of ingestion.
- Potential Health Risks
Exposure to lead in drinking water poses significant health risks, especially to vulnerable populations such as children and pregnant women. Lead ingestion can lead to neurological and developmental issues, including learning disabilities and reduced IQ in children. In adults, lead exposure may result in cardiovascular problems, kidney damage, and reproductive issues.
3. PFAS (Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances)
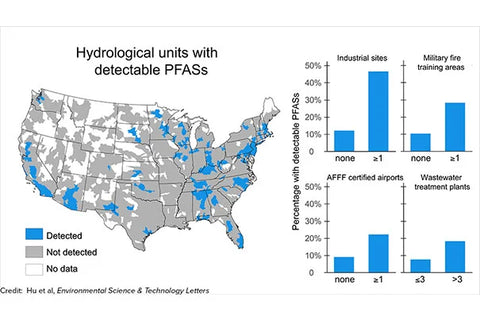
PFAS are synthetic chemicals used in various industrial and consumer products, including firefighting foam, non-stick cookware, and waterproofing treatments. These "forever chemicals" are known for their persistence in the environment and have been associated with numerous health concerns, including cancer, liver damage, and immune system disruption.
- Source
Industrial Discharges: PFAS compounds are used in various industrial processes, including manufacturing of non-stick cookware, waterproof fabrics, and firefighting foam, leading to contamination of water bodies.
Landfills and Waste Sites: Disposal of products containing PFAS, as well as firefighting foam runoff, can contaminate groundwater near landfills and waste sites.
Aqueous Film-Forming Foam (AFFF): Military and firefighting operations often use AFFF containing PFAS, leading to contamination of soil and water in surrounding areas.
- Potential Health Risks
Chronic exposure to PFAS has been linked to various adverse health effects, including cancer (particularly kidney and testicular cancer), liver damage, thyroid disorders, decreased fertility, developmental delays in infants and children, and compromised immune system function. Additionally, PFAS are known as "forever chemicals" due to their persistence in the environment, posing long-term health risks even at low concentrations.
4. Nitrates
Nitrates are primarily introduced into water sources through agricultural runoff and sewage. High levels of nitrates in drinking water can pose significant health risks, particularly to infants, as they can interfere with the blood's ability to carry oxygen, leading to methemoglobinemia or "blue baby syndrome."
- Source
Agricultural Runoff: The use of nitrogen-based fertilizers in agriculture can result in the leaching of nitrates into groundwater and surface water.
Animal Waste: Livestock operations produce significant amounts of nitrogen-rich waste, which can contaminate nearby water sources through runoff.
Septic Systems: Improperly maintained or failing septic systems can release nitrates into the groundwater, particularly in rural areas without access to centralized sewage treatment.
- Potential Health Risks
High levels of nitrates in drinking water pose significant health risks. Nitrate ingestion can lead to methemoglobinemia, a condition where oxygen-carrying capacity of blood is impaired, particularly dangerous for infants, causing "blue baby syndrome." Additionally, chronic exposure to nitrates has been linked to adverse effects on cardiovascular health, gastrointestinal issues, and reproductive problems. Pregnant women and individuals with compromised immune systems are particularly vulnerable.
Top Blogs Related to Solving Toxic Chemicals in Drinking Water You Can't Miss!
If you want to delve into how to address each individual toxic chemical mentioned above in detail, you definitely shouldn't miss our comprehensive previous blog post as below. If you don't have time to read through each one, you can skip directly to our next section to get the best general solutions.
1. Best Water Filter for Arsenic
2. Can Boiling Water Get Rid of Lead?
3. How to Remove Lead From Water?
4. How to Remove PFAS From Water at Home?
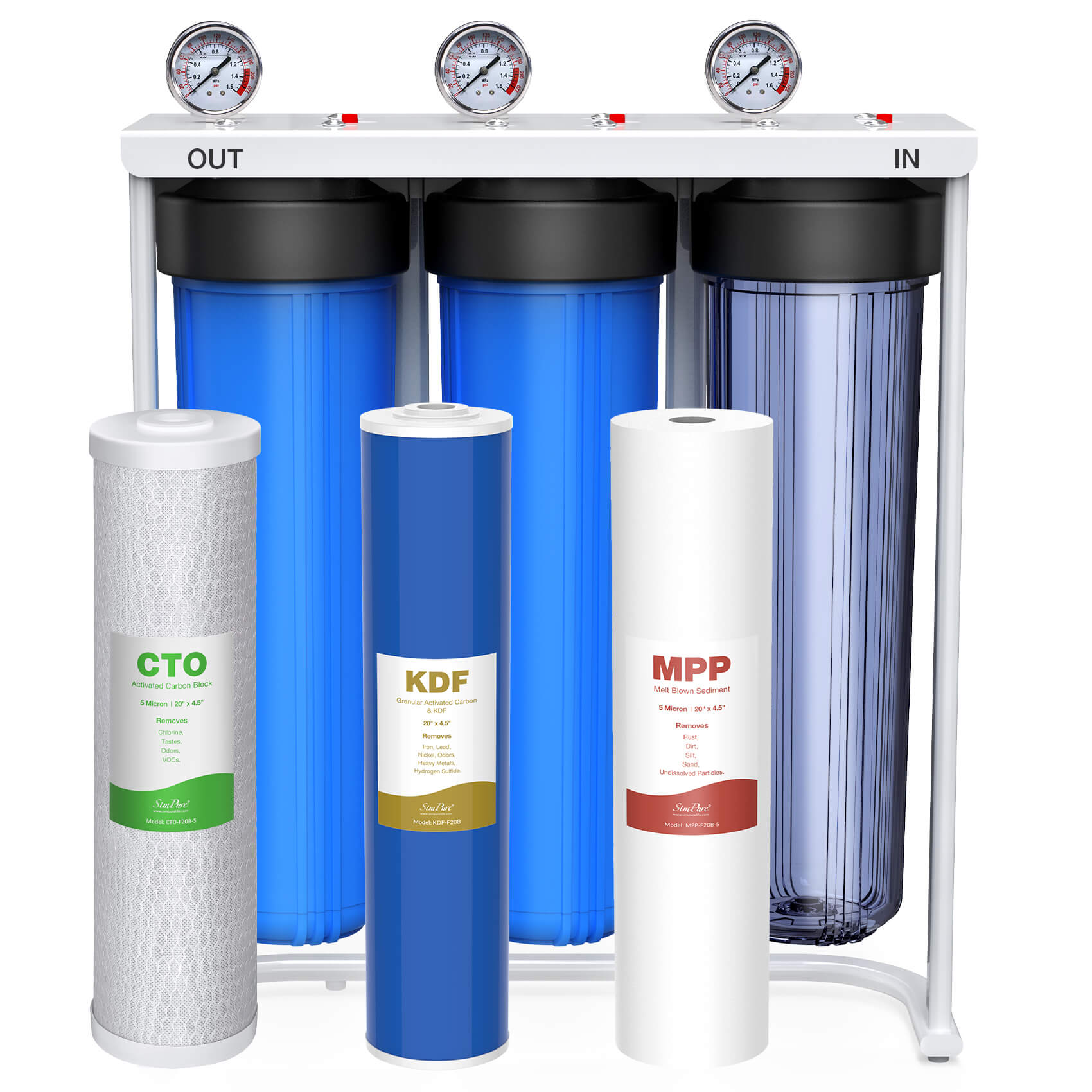
Best Solutions for Toxic Chemicals Removal in US Drinking Water: RO Technologies
Amid growing concerns over the presence of toxic chemicals in US drinking water, finding effective solutions is paramount to safeguarding public health. Fortunately, advancements in water treatment technologies offer promising avenues for addressing these contaminants. Among the various water filtration systems available, reverse osmosis stands out as a highly efficient and reliable solution for effectively removing a wide range of pollutants, including arsenic, lead, PFAS, and nitrates.

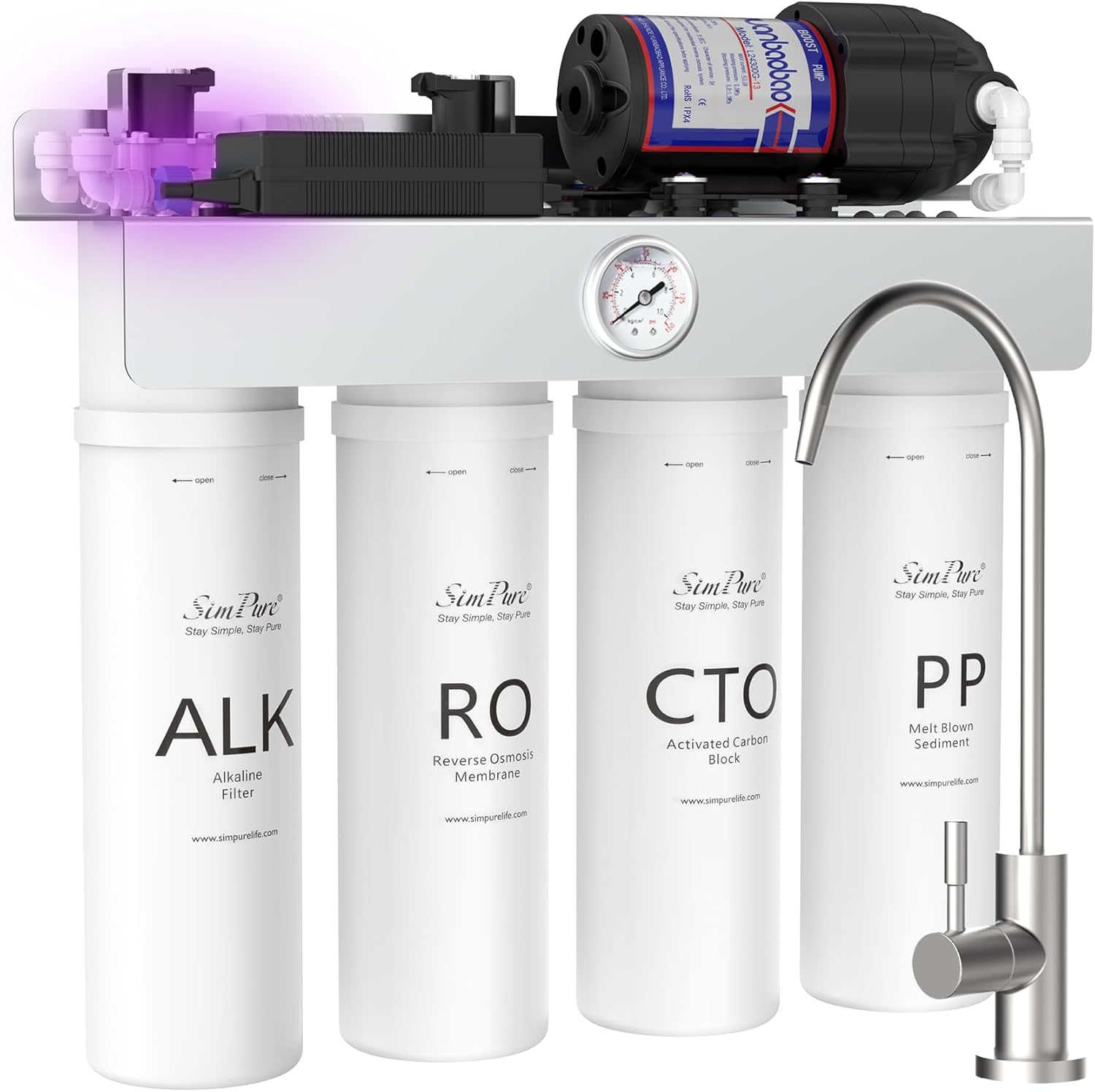
Reverse osmosis systems employ a sophisticated filtration process that relies on a semi-permeable membrane [typically ranges from 0.0001 to 0.001 microns.] to selectively remove contaminants from water. This membrane acts as a barrier, allowing only water molecules to pass through while trapping and eliminating dissolved solids, chemicals, and other impurities present in the water.

One of the key advantages of RO systems is their exceptional contaminant removal efficiency. The semi-permeable membrane used in RO filtration is capable of trapping even the smallest particles, including microscopic traces of arsenic, lead, PFAS, and nitrates. Moreover, RO systems offer versatile application possibilities, making them suitable for both residential and commercial settings. Whether installed under the kitchen sink or integrated into a larger water treatment system, RO units can effectively address the diverse needs of households, businesses, and communities.

Additionally, RO systems are relatively low-maintenance and cost-effective over the long term. While initial installation may require an investment, the ongoing operational expenses are minimal compared to the health benefits and peace of mind provided by clean, purified water.
In summary, ensuring access to safe drinking water requires collective effort and informed action. Advocating for clean water policies and investing in filtration systems, such as reverse osmosis technology, are crucial steps towards mitigating the risks of toxic chemicals like arsenic, lead, PFAS, and nitrates. For an effective filtration solution, choose SimPure reverse osmosis system, offering countertop, undersink, and tankless options, all equipped to eliminate up to at least 96%+ removal rate of harmful contaminants. Check the specific toxic chemical removal rate at our SGS report in each RO systems product page! Here is an example of our best selling RO system product SimPure Y7P series test report for toxic chemical and more...
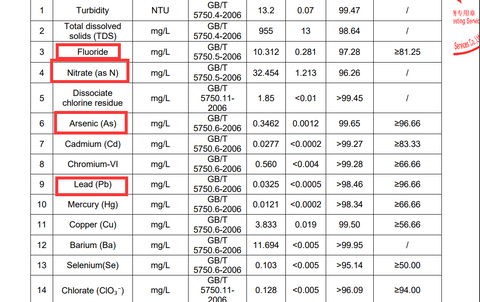
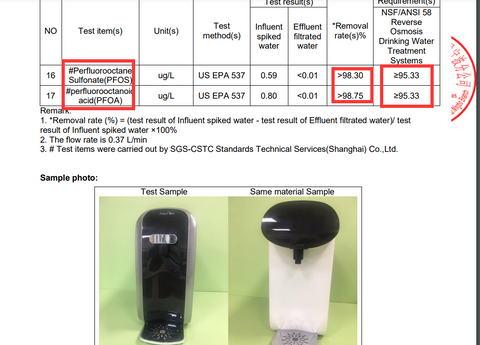
Get the full test report at:
https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0407/1692/7132/files/SimPure_Y7P_SGS_Test_Report.pdf?v=1684975097