In times of emergencies, getting clean and safe drinking water is one of the most critical factors for survival. Natural disasters, power outages, and other unforeseen events can disrupt water supplies, leaving individuals and families vulnerable to dehydration and waterborne illnesses. As part of any comprehensive emergency preparedness plan, investing in reliable outdoor water filtration systems is essential. This article explores the importance of water filters for emergency preparedness, the types available, and key considerations when selecting the right option for your needs.
Importance of Water Filters in Outdoor Emergencies
 Water is a fundamental human necessity. While the average person can survive for weeks without food, survival without water is limited to just a few days. (Suggested reading: How Long Can A Human Survive Without Water.) During emergencies, municipal water supplies may become contaminated with bacteria, viruses, chemicals, or other harmful substances. Additionally, natural sources such as rivers, lakes, or wells may not be safe for consumption without proper treatment.
Water is a fundamental human necessity. While the average person can survive for weeks without food, survival without water is limited to just a few days. (Suggested reading: How Long Can A Human Survive Without Water.) During emergencies, municipal water supplies may become contaminated with bacteria, viruses, chemicals, or other harmful substances. Additionally, natural sources such as rivers, lakes, or wells may not be safe for consumption without proper treatment.
A dependable outdoor water filtration system ensures access to clean drinking water, reducing the risk of waterborne diseases such as cholera, dysentery, and giardiasis. It also provides peace of mind, allowing you to focus on other aspects of survival and recovery during a crisis.
Types of Emergency Water Filters
There are several types of water filtration systems designed for emergency situations. Each type has its advantages and limitations, making it important to choose one that aligns with your specific needs and circumstances.
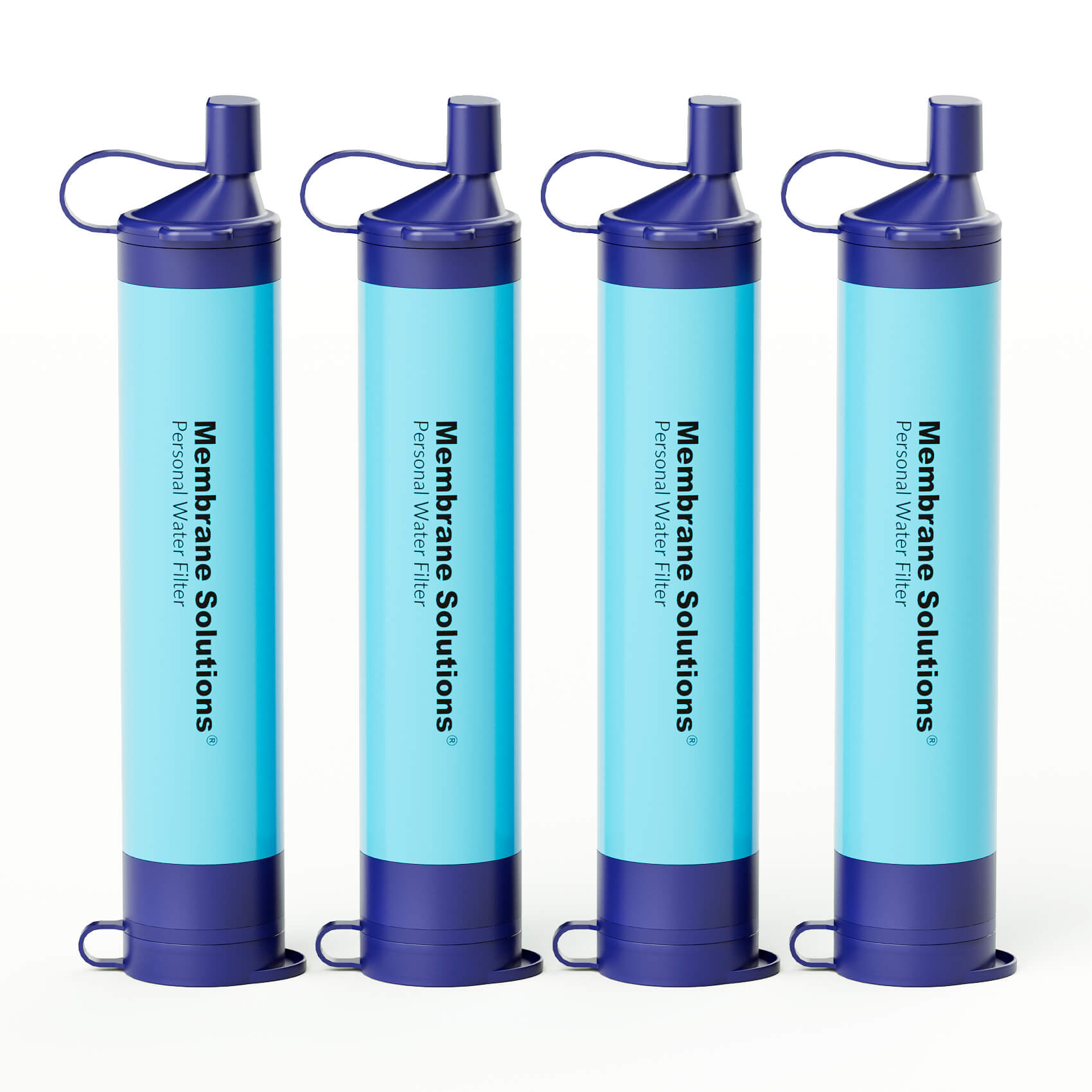
1. Straw Filters
Straw filters are compact, lightweight, and easy to use, making them a popular choice for emergency kits and outdoor survival. These filters allow users to drink directly from a water source, such as a stream or puddle, by filtering out bacteria and protozoa as the water passes through the straw.
- Advantages: Portable, affordable, and simple to use.
- Limitations: Not suitable for filtering large quantities of water or removing viruses and chemical contaminants.
2. Pump Filters
 Pump filters use a manual pumping mechanism to draw water through a filtration system. They are effective at removing bacteria, protozoa, and some chemicals, making them ideal for treating water from natural sources.
Pump filters use a manual pumping mechanism to draw water through a filtration system. They are effective at removing bacteria, protozoa, and some chemicals, making them ideal for treating water from natural sources.
-Advantages: Capable of filtering larger volumes of water and suitable for group use.
-Limitations: Requires effort to operate and may not remove viruses unless equipped with an additional purification step.
3. Gravity Filters
Gravity-fed systems rely on gravity to pull water through a filter, eliminating the need for manual pumping. These systems are often used in base camps or stationary setups during emergencies.
- Advantages: Ideal for filtering large quantities of water with minimal effort.
- Limitations: Bulky and less portable compared to other options.
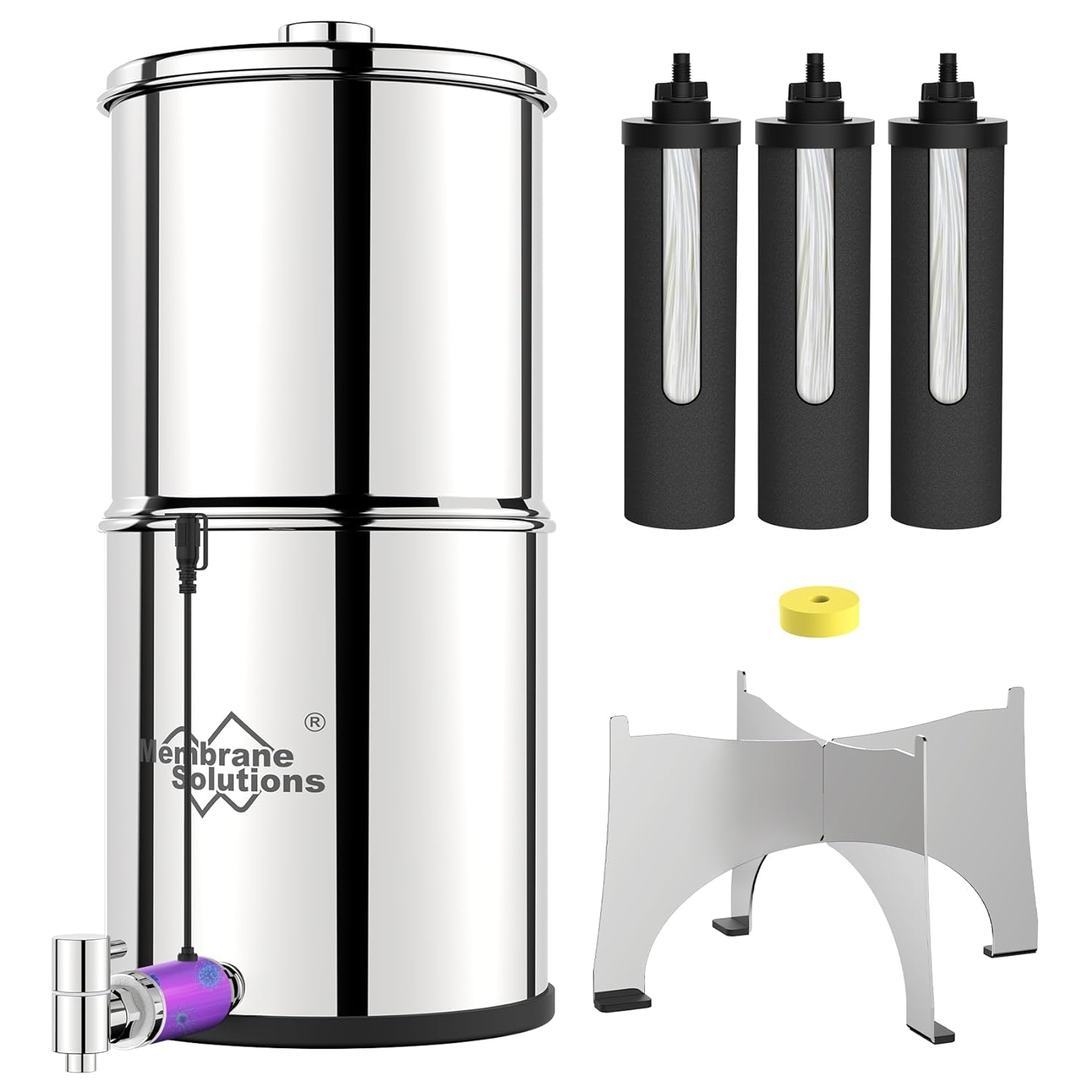
If you live off-grid or prep for long-term emergencies, the Memebrane Solutions U3P stainless steel gravity water filter is a must. It holds 2.25 gallons and filters without electricity—just pour in water and let gravity do the work. The 3-stage filters remove bacteria, sediment, and chemicals using a 0.1μm membrane and carbon block. You get clean, fresh-tasting water from almost any source. Its food-grade steel tank is built to last and includes a stable stand and leak-proof spigot. With a 9,000-gallon lifespan and no complicated setup, it’s perfect for daily off-grid use or emergency water storage.
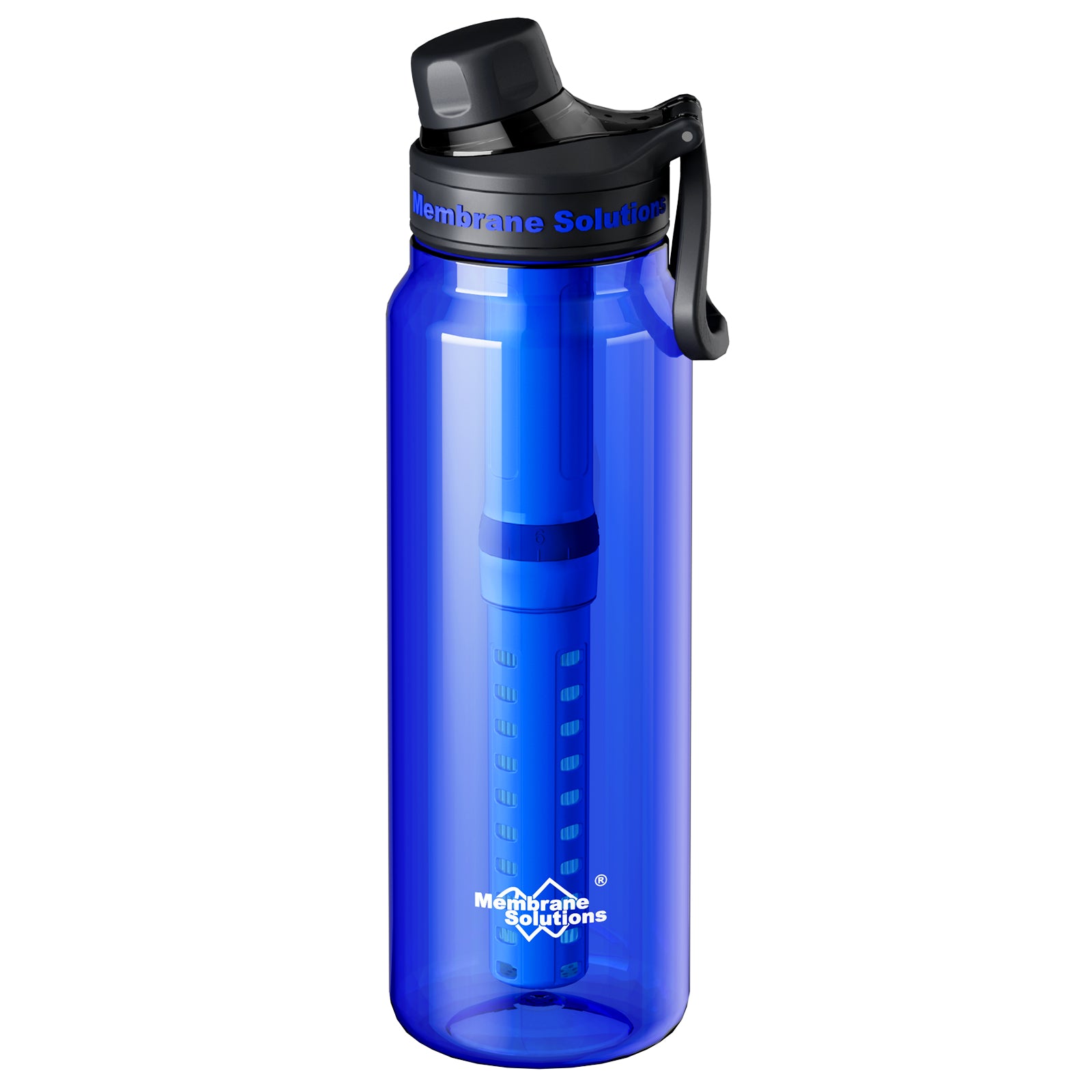
4. Bottle Filters

Water bottles with built-in filters like Membrane Solutions C3 series are convenient for individuals on the move. These bottles allow users to fill them with untreated water, which is filtered as they drink. They look like regular water bottles but have built-in filters that remove bacteria, parasites, and dirt. Just fill the bottle from a stream or lake, screw on the lid, and drink. As you sip, the filter cleans the water instantly. It’s that easy—no waiting, no pumping, no electricity. Some models also reduce chemicals and bad taste. These bottles are lightweight and fit easily in a backpack. If you get lost or run out of clean water, a bottle filter can keep you safe and hydrated on the go.
- Advantages: Lightweight, portable, and easy to use.
- Limitations: Limited capacity and may not remove all contaminants.
5. Ultraviolet (UV) Purifiers
In emergencies like floods, earthquakes, or water supply failures, UV purifiers offer fast and effective water disinfection. If the tap water looks clear but may be unsafe, a UV purifier can kill up to 99.99% of germs. You just shine the UV light into your water container for about a minute. It needs batteries or USB charging, but no chemicals, filters, or waiting time. It's perfect when you're at home or sheltering somewhere with access to clear but untrustworthy water. Always pre-filter like water filter straw cloudy water first, as UV only works well on clear water.
- Advantages: Highly effective against microorganisms.
- Limitations: Requires batteries or a power source and does not remove chemical contaminants or sediment.
6. Ceramic Filters
Ceramic filters use porous ceramic material to trap contaminants such as bacteria and protozoa. They are durable and can be cleaned for extended use.You just pour water into the filter or pump it through, and the ceramic element traps harmful particles. Most ceramic filters can be cleaned and reused, which is helpful when you're away from supplies. They don’t need electricity, so they work anywhere.
- Advantages: Long-lasting and effective against most pathogens.
- Limitations: Slower filtration rate and less effective against viruses.
7. Portable Reverse Osmosis Systems
Compact reverse osmosis systems use pressure to force water through a semi-permeable membrane that removes a wide range of contaminants, including bacteria, viruses, chemicals, and heavy metals. Unlike basic filters, RO systems offer advanced purification, making them ideal for emergency kits, camping, and survival scenarios. They often require no electricity and operate manually or with minimal power, making them practical in off-grid situations.
- Advantages: Produces highly purified water.
- Limitations: Expensive, requires power or manual effort, and generates wastewater
Key Considerations When Choosing a Water Filter

Selecting the right water filter for emergency preparedness involves evaluating several factors:
1. Filtration Capabilities
Understand the types of contaminants the filter can remove. Look for systems that address bacteria, protozoa, viruses, chemicals, heavy metals, and sediment based on your anticipated needs.
2. Portability
For emergencies requiring evacuation or mobility, lightweight and compact filters such as straw filters or bottle filters are ideal. For stationary situations like sheltering in place, gravity filters or larger systems may be more suitable.
3. Capacity
Consider how much water you will need to filter daily for yourself or your group. Some filters are designed for individual use, while others can handle larger volumes.
4. Ease of Use
In high-stress situations, simplicity is key. Choose a filter that is easy to operate without requiring extensive setup or technical knowledge.
5. Durability
Emergency scenarios can be unpredictable and harsh. Opt for filters made from durable materials that can withstand rough conditions.
6. Maintenance Requirements
Some filters require regular cleaning or replacement parts such as cartridges or membranes. Ensure you have access to spare components or choose a low-maintenance option.
7. Shelf Life
For long-term preparedness, select filters with a long shelf life so they remain effective when needed.
8. Cost
Emergency preparedness is an investment in safety. While it's important to stay within budget, prioritize quality and reliability over cost alone.
Supplementing Water Filters with Purification Methods
While water filters are effective at removing many contaminants, certain situations may require additional purification steps:
- Boiling
Boiling water for at least 1 minute kills bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
Ideal as a backup when filters or purifiers aren’t available.
Requires fuel and time, so plan accordingly.
- Chemical Treatment (Chlorine or Iodine Tablets)
Easily carried and lightweight, these tablets kill many microorganisms.
Follow instructions carefully for correct dosage and wait time (usually 30 minutes).
Not effective against all parasites and may alter taste.
- Activated Carbon Filters (Standalone or Combo)
Removes chlorine, bad odors, and some chemicals.
Usually paired with other filtration steps to improve taste and quality.
- Distillation
Boils water and collects condensed steam, leaving contaminants behind.
Removes salts, heavy metals, and microbes.
Requires special equipment and energy.
- Solar Disinfection (SODIS)
Exposes water in clear bottles to sunlight for 6+ hours to kill pathogens.
Low-cost and portable but requires sunlight and clear water.
Water filters are an indispensable component of any emergency preparedness plan. With various types of filters available on the market, it's important to assess your specific needs and choose a system that aligns with your circumstances.
Proper planning today can make all the difference in safeguarding your health and well-being tomorrow. Equip yourself with reliable water filtration solutions to stay prepared for whatever challenges may come your way.