Did you know that the water you drink every day may pose a health risk? Seemingly clear tap water may carry hundreds of contaminants, including bacteria and viruses that are invisible to the naked eye!
Whether it is water transported by the municipal pipeline network or groundwater extracted from deep wells, these sources of life may be contaminated by pathogenic microorganisms during the transportation process, becoming invisible killers that threaten the health of the whole family.
Although the water system ensures the safety baseline of daily water use through strict control when accidents such as aging of pipes and failure of disinfection occur, what may flow out of your tap may be not only clean water but also a legion of microorganisms that exceed the standard - they are waiting for an opportunity to break through the human body's defense system. It’s closely related to life. So what filtering technologies do we have to deal with these problems? As we all know, RO is now a very common technology. But Can the RO system remove bacteria and viruses from tap water? Just keep reading!

What is a Contaminant in the Drinking Water?
We know that there are many kinds of water contaminants, and their behaviors, sizes, and shapes vary greatly. Therefore, different filtration methods have different effects in removing certain contaminants. Microorganisms such as bacteria/viruses are a type of contaminant that people are very worried about. We often hear questions like: Does a RO system remove bacteria and viruses from tap water? As people pay more and more attention to water safety and the demand for deep purification, it is worthy of our common attention and today, we will discuss it.
According to the Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA), US EPA was originally passed by Congress in 1974 to protect public health by regulating the nation's public drinking water supply.
In narrow definition, "contaminant" means any physical, chemical, biological, or radiological substance or matter in water. Therefore, the law defines "contaminant" very broadly as being anything other than water molecules
Types of Drinking Water Contaminants
SDWA defines the contaminants as include
- Physical contaminants, Physical pollutants mainly refer to suspended and insoluble substances that can be seen by the naked eye or detected by physical means, such as silt, suspended particles, metal debris, plastic particles, etc.
- Chemical contaminants, Chemical pollutants are elements or compounds. These contaminants may be naturally occurring or man-made, such as Heavy metals in inorganic substances, such as lead, mercury, and arsenic, which are all harmful substances. Organic substances include benzene, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, etc., which come from petrochemical or combustion processes, pesticides, drug residues, and disinfection by-products.
- Biological contaminants mainly include microorganisms or microbial pollutants in the water such as bacteria, viruses, parasites, algae, etc. (ie: Vibrio cholerae, Legionella, Escherichia coli, Norovirus, Cryptosporidium, Giardia...) These microorganisms may cause diseases, such as cholera, dysentery, etc.
· Radiological contaminants, Radioactive pollutants can be divided into two categories: natural and artificial. Natural sources include uranium, radium, etc., which may come from geological structures; Artificial sources include nuclear accidents, and medical and industrial waste, such as cesium-137 in Fukushima nuclear wastewater.
Do RO Purifiers Kill Viruses & Bacteria in Water?
The core principle of reverse osmosis filtration is that whether pollutants can be intercepted depends on their size compared to the RO membrane pore size. The effectiveness of reverse osmosis filters for various pollutants depends on the size of these pollutants. For a details explanation of RO purifiers, please refer to the following.
A reverse osmosis filter has a pore size of about 0.0001 micron

1. Working principle:
Use a high-pressure water pump to force the dirty water to "go backward" through multiple layers of filter nets, and finally only release pure water molecules.
2. Visualization of filtration accuracy:
The pore size of the RO membrane (0.0001 microns)is ≈ **one-millionth of a hair**
- Parasites (5 microns) → It is equivalent to a truck not being able to crash into a bicycle lane
- Bacteria (0.5 microns) → Like a basketball stuck in a security net
- Viruses (0.02 microns) → Like a mosquito trapped in a screen window
So if there are bacteria, viruses, and microorganisms in your tap water, and your water is filtered through a reverse osmosis system, the bacteria will not pass through the filter because they are too large to fit through the pores of the membrane. In other words, reverse osmosis filters do remove bacteria from tap water.
So we conclude that the reverse osmosis system removes:
• Parasites
• Bacteria
• Viruses
Besides, Reverse osmosis systems will remove some types of chemicals from water, including lead, copper, chromium, chloride, and sodium (salt). They may also reduce levels of arsenic, fluoride, radium, sulfate, calcium, magnesium, potassium, nitrate, and phosphorous.
RO Purification: Your Molecular Guardian Against Waterborne Threats
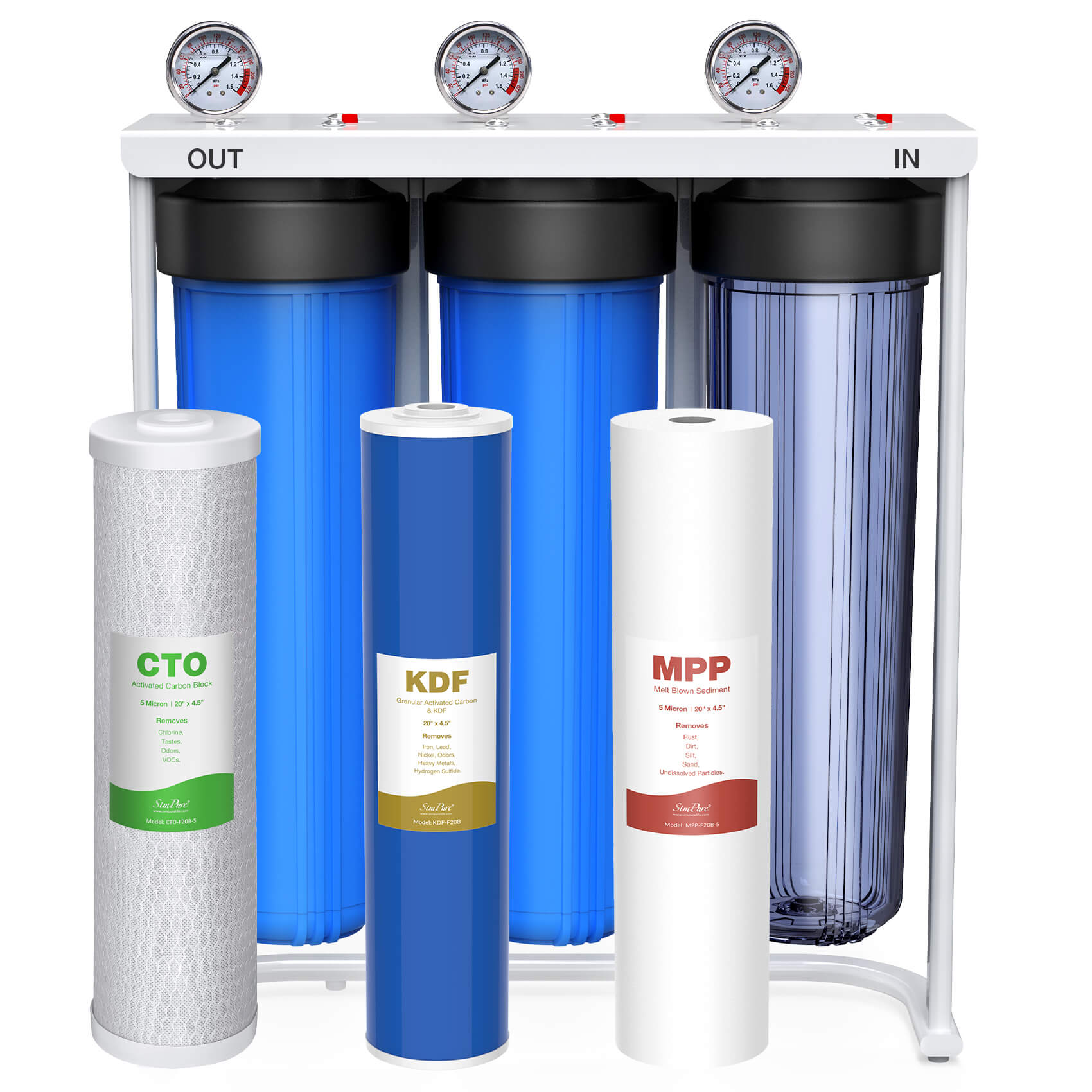
Through rigorous multi-stage filtration, RO systems act as an impenetrable shield—eliminating over 99.9% of pathogens, including stealthy viruses (as tiny as 0.02 microns) and antibiotic-resistant bacteria, as well as most of the RO systems with multiple-layer filtration stage like the below
- Pre-Filtration: traps sediment
- Carbon Block: neutralizes chlorine & chemicals at the molecular level
- RO Membrane (0.0001μm pores) —only permitting water molecules to pass
- Post-Carbon: erases any residual tastes
- Remineralization: adds essential electrolytes
Check SimPure Countertop/Under sink RO system (Y7P, Y9, Y10, T1-400…)
Bonus: Adding UV sterilization will further protect your water safety

While reverse osmosis is very effective at removing bacteria from water, in rare cases where bacterial contamination is particularly prevalent or for some products that have pure water storage tanks, some additional measures can be taken to fully protect your water. In this case, UV lights can be added after the water passes through the reverse osmosis filter, which will kill any residual bacteria that may have passed through. Jsut Check SimPure T1-400UV, Y7P Series UV model.
In general, RO machines can effectively remove microorganisms such as bacteria and viruses in tap water and also have a good removal effect on other drinking water contaminants and chemical pollutants, etc. If you have any questions about choosing a reverse osmosis system model, check the SimPure official shop and all our RO models have the SGS report that indicates the performance and what contaminant can be removed. SimPure professional engineers will provide you with 24-hour services.